Securing funding is a tall order for any enterprise. If you happen to’re within the thick of that course of, it is advisable to have a grasp on some key metrics and sticking factors — one in every of them being one thing often known as your leverage ratio.

Right here, we’ll discover the idea a bit additional, evaluate a few of the ratios that fall below the broader “leverage ratio” umbrella, see what a strong one appears like, and try some examples.
Skip to:
Leverage Ratio
The time period ‘leverage ratio’ refers to a set of ratios that spotlight a enterprise’s monetary leverage when it comes to its belongings, liabilities, and fairness. They present how a lot of a corporation’s capital comes from debt — a strong indication of whether or not a enterprise could make good on its monetary obligations.
A better monetary leverage ratio signifies that an organization is utilizing debt to finance its belongings and operations — usually a telltale signal of a enterprise that could possibly be a dangerous wager for potential traders.
It may well imply that earnings shall be inconsistent, it could possibly be some time earlier than shareholders can see a significant return on their funding, or the enterprise might quickly be bancrupt.
Collectors additionally depend on these metrics to find out whether or not they need to lengthen credit score to companies. If an organization’s monetary leverage ratio is extreme, it means they’re allocating most of its money circulation to paying off money owed and is extra susceptible to defaulting on loans.
A decrease monetary leverage ratio is normally a mark of a financially accountable enterprise with a gentle income stream. Even when an organization behind it’s working vital money owed, an distinctive monetary leverage ratio tells potential shareholders and credit score companies {that a} enterprise poses minimal threat and is probably going price an funding.
Easy Leverage Ratio: Debt-to-Asset
One of many easiest leverage ratios a enterprise can measure is its debt-to-asset ratio. This ratio reveals how a lot an organization makes use of debt to finance its belongings.
You’ll be able to calculate this metric by dividing the whole debt—each short-term and long-term, by whole belongings.
Debt-to-Asset Ratio = Complete Debt (quick time period + long run)/Complete Belongings
With this measurement, you possibly can higher consider how financially secure an organization is, and use this metric to check different corporations throughout the identical trade. A excessive debt-to-asset ratio might imply an organization is extra vulnerable to defaulting on its loans.
What is an efficient monetary leverage ratio?
A super monetary leverage ratio varies by the sort of ratio you are referencing. With some ratios — just like the curiosity protection ratio — larger figures are literally higher. However for probably the most half, decrease ratios are likely to mirror higher-performing companies.
As an example, with the debt-to-equity ratio — arguably probably the most distinguished monetary leverage equation — you need your ratio to be under 1.0. A ratio of 0.1 signifies {that a} enterprise has just about no debt relative to fairness and a ratio of 1.0 means an organization’s debt and fairness are equal. Typically, a very sound one will fall between 0.1 and 0.5.
A ratio of 0.5 — a sign {that a} enterprise has twice as many belongings because it has liabilities — is taken into account to be on the upper boundary of fascinating and comparatively frequent. That stated, what could be thought of a “frequent” determine varies from case to case, in accordance with components like an organization’s scale, maturity, and trade.
What’s a excessive leverage ratio?
What is taken into account a excessive leverage ratio will depend upon what ratio you’re measuring. For instance, a complete debt-to-assets ratio larger than 1 could be thought of excessive – that means an organization has extra liabilities than belongings.
Equally, a debt-to-equity ratio larger than 2 would even be thought of excessive. Subsequent, we’ll look into companies the place excessive leverage ratios are frequent.
Companies With Larger Leverage Ratios
A typical startup usually has to incur vital money owed to get off the bottom and allocate a good portion of its money circulation to settle them — making for larger monetary leverage ratios. Companies with larger manufacturing prices additionally are likely to run larger debt-to-equity ratios than most others.
Past that, sure industries lend themselves to larger common monetary leverage ratios. In these circumstances, you possibly can gauge the soundness of an organization’s monetary leverage by evaluating it to these of its opponents.
For instance, companies in capital-intensive industries — like oil and fuel or telecommunications — usually should sink vital monetary assets into infrastructure and upkeep, making for big investments that may inflate debt-to-equity figures.
Learn how to Calculate Leverage Ratio
There are just a few several types of leverage ratios that fall below the “monetary leverage ratio” umbrella. This is find out how to calculate a few of them, utilizing information discovered in your stability sheet or basic ledger:
Forms of Leverage Ratios
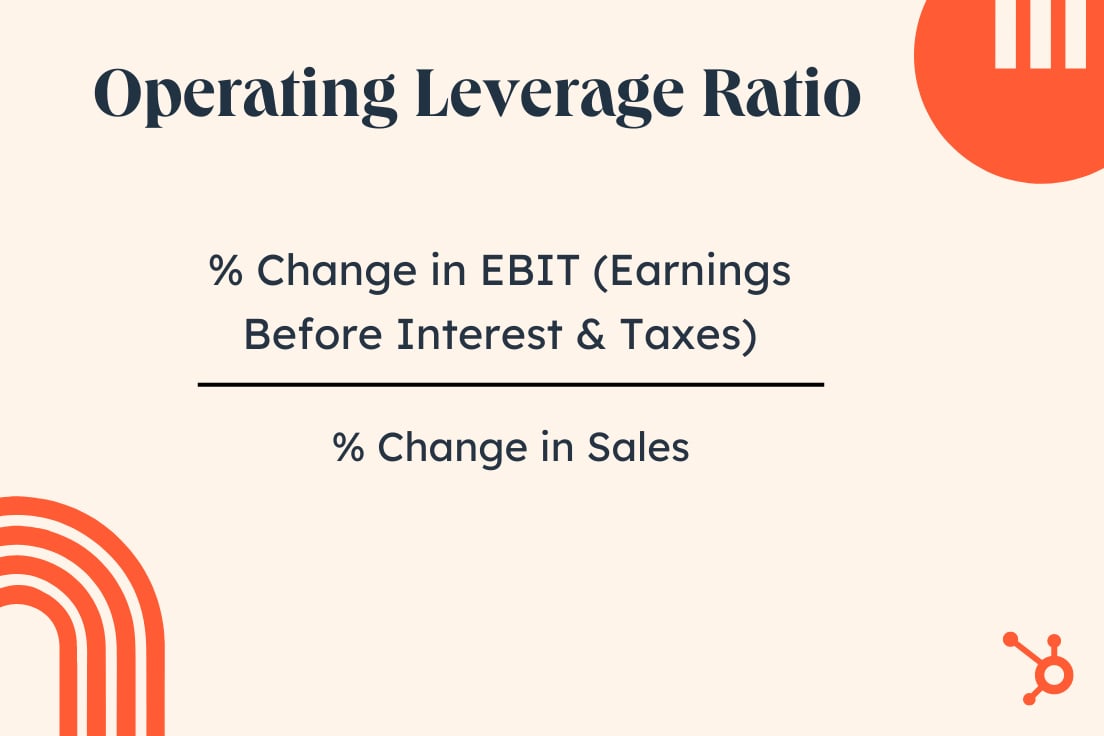
1. Working Leverage Ratio
The working leverage ratio measures the ratio of a enterprise’ contribution margin to its web working earnings. It evaluates how a lot a enterprise’ earnings adjustments relative to adjustments in gross sales. It is calculated utilizing the next components:
Working Leverage Ratio = % change in EBIT (earnings earlier than curiosity and taxes) / % change in gross sales
2. Web Leverage Ratio
Web leverage ratio, or web debt to EBITDA (earnings earlier than curiosity, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) measures the ratio of a enterprise’ debt to earnings. It displays how lengthy it might take a enterprise to pay again its debt if debt and EBITDA have been fixed. It is calculated utilizing the next components:
Web Leverage Ratio = (Web Debt – Money Holdings) / EBITDA
3. Debt-to-EBITDAX
Much like the web leverage or debt-to-EBITDA ratio is the EBITDAX. EBITDAX is earnings earlier than curiosity, taxes, depreciation, and amortization earlier than exploration bills. This ratio is primarily geared in direction of oil and fuel corporations that incur exploration bills from researching areas to drill and prices of drilling. As such, these corporations require a lot of capital to cowl labor, tools, and different associated prices.
This metric measures an organization’s capacity to generate earnings from its operations and repair money owed.
To calculate your EBITDAX:
EBITDAX = EBIT + Depreciation + Amortization + Exploration Bills
4. Debt-to-Fairness Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio measures the ratio of a enterprise’ whole liabilities to its stockholders’ fairness. It provides an at-a-glance take a look at the worth of a enterprise relative to its money owed. It is calculated utilizing the next components:
Debt-to-Fairness Ratio = Liabilities / Stockholders’ Fairness
5. Debt-to-Capital Ratio
This metric is used to guage an organization’s monetary construction and the way it’s financing its operations. On this case, it takes under consideration each short-and long-term debt, and capital refers to shareholder fairness. You’ll be able to calculate it with the next components:
Debt-to-Capital Ratio = Debt/(Debt + Shareholders Fairness)
6. Debt-to-Capitalization
Capitalization refers back to the sum of money an organization raises to buy belongings that they then use to drive a revenue. An organization can elevate this cash through the use of debt or promoting inventory to its shareholders.
The debt-to-capitalization ratio measures the quantity of debt an organization makes use of to finance its belongings in comparison with the quantity of fairness used to finance its belongings.
Debt-to-Capitalization Ratio = (Quick-term Debt + Lengthy-term Debt)/(Quick-term Debt + Lengthy-term Debt+ Shareholder Fairness)
A excessive debt-to-capitalization ratio might point out that an organization has a better threat of insolvency as a consequence of being over-leveraged.
7. Curiosity Protection Ratio
One of many caveats of reviewing whole debt liabilities for an organization is that it doesn’t bear in mind the corporate’s capacity to service or pay again its money owed. This is a matter the curiosity protection ratio fixes.
Curiosity Protection Ratio = Working Earnings/Curiosity Bills
The curiosity protection ratio demonstrates an organization’s capacity to make curiosity funds. Though it varies by trade, an curiosity protection ratio of three and up is most popular.
8. Fastened-Charged Protection Ratio
The fixed-charge protection ratio measures how seemingly an organization will pay its fastened prices from earnings earlier than curiosity owed and taxes. Fastened prices can embrace lease funds, mortgage funds or any expense that’s fastened or is similar cost quantity every month. To calculate it, take the EBIT (earnings earlier than curiosity and taxes) and divide it by the curiosity expense of long-term debt.
Merely put, the fixed-charges protection ratio reveals what number of occasions an organization can cowl its predictable month-to-month monetary obligations.
Monetary Leverage Ratio Examples
Listed here are some examples of what monetary leverage ratios can appear to be in follow.
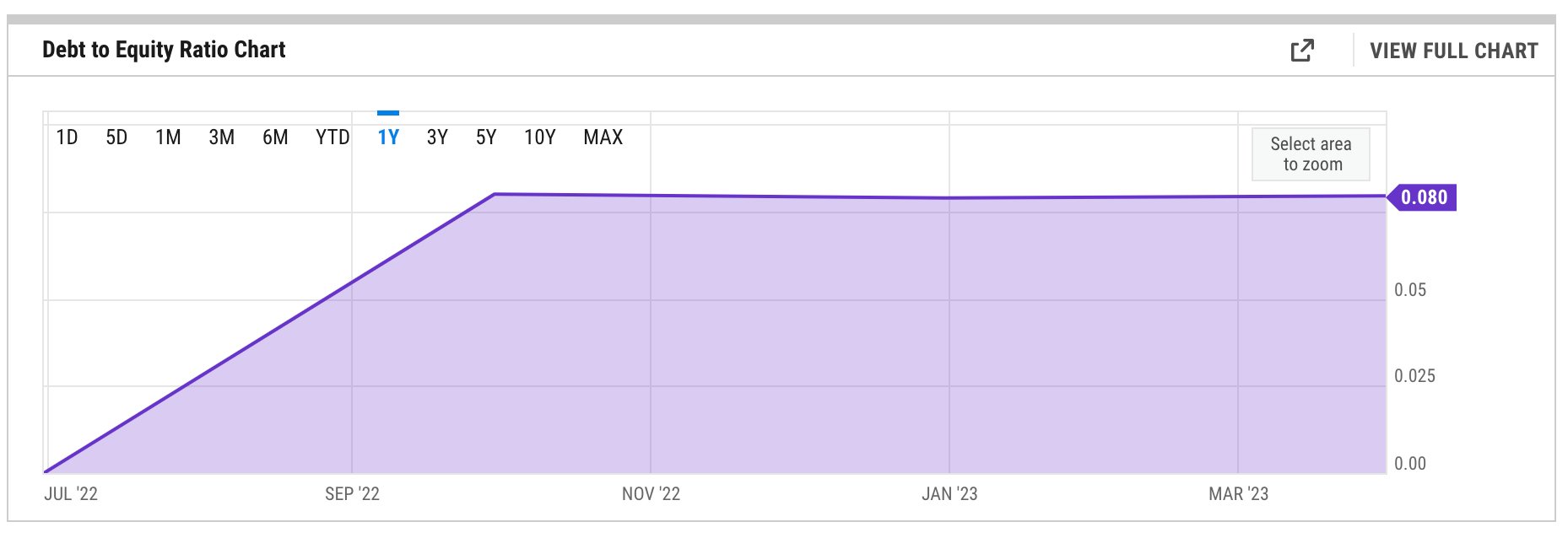
1. Meta’s 2023 Debt-to-Fairness Ratio
As you possibly can see from this chart, Meta has a debt-to-equity ratio of .080. As this ratio is below 1, Meta (Fb’s and Instagram’s mother or father firm) is in a fairly wholesome state in terms of managing its liabilities.
2. Apple’s 2021 Debt-to-Fairness Ratio
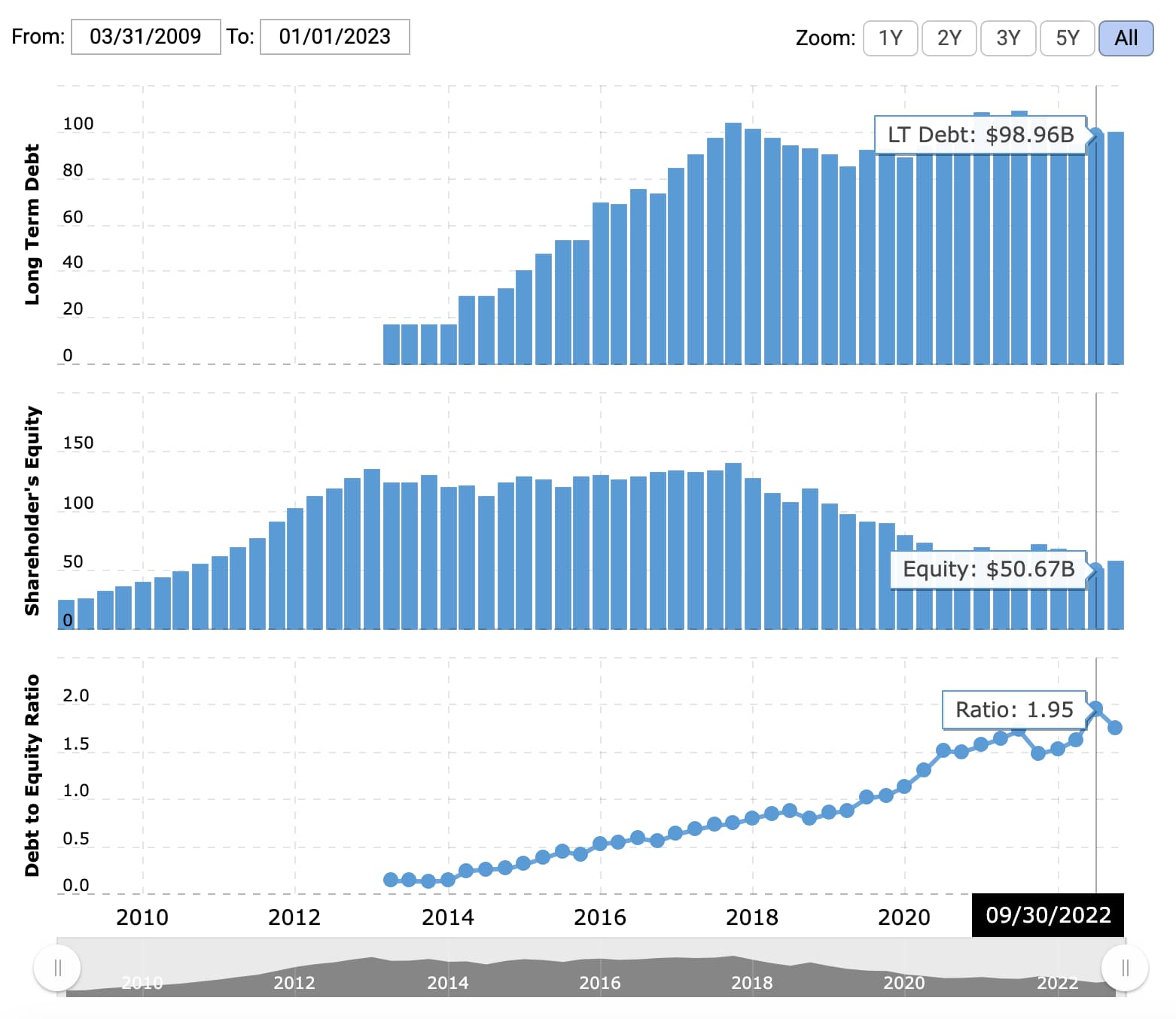
Although Apple’s present debt-to-equity ratio is above 1.0, on no account is it unmanageable or alarming. Plus, it is Apple — shareholders in all probability aren’t too apprehensive concerning the firm’s liabilities getting uncontrolled.
3. Verizon’s 2015 Debt-to-Fairness Ratio
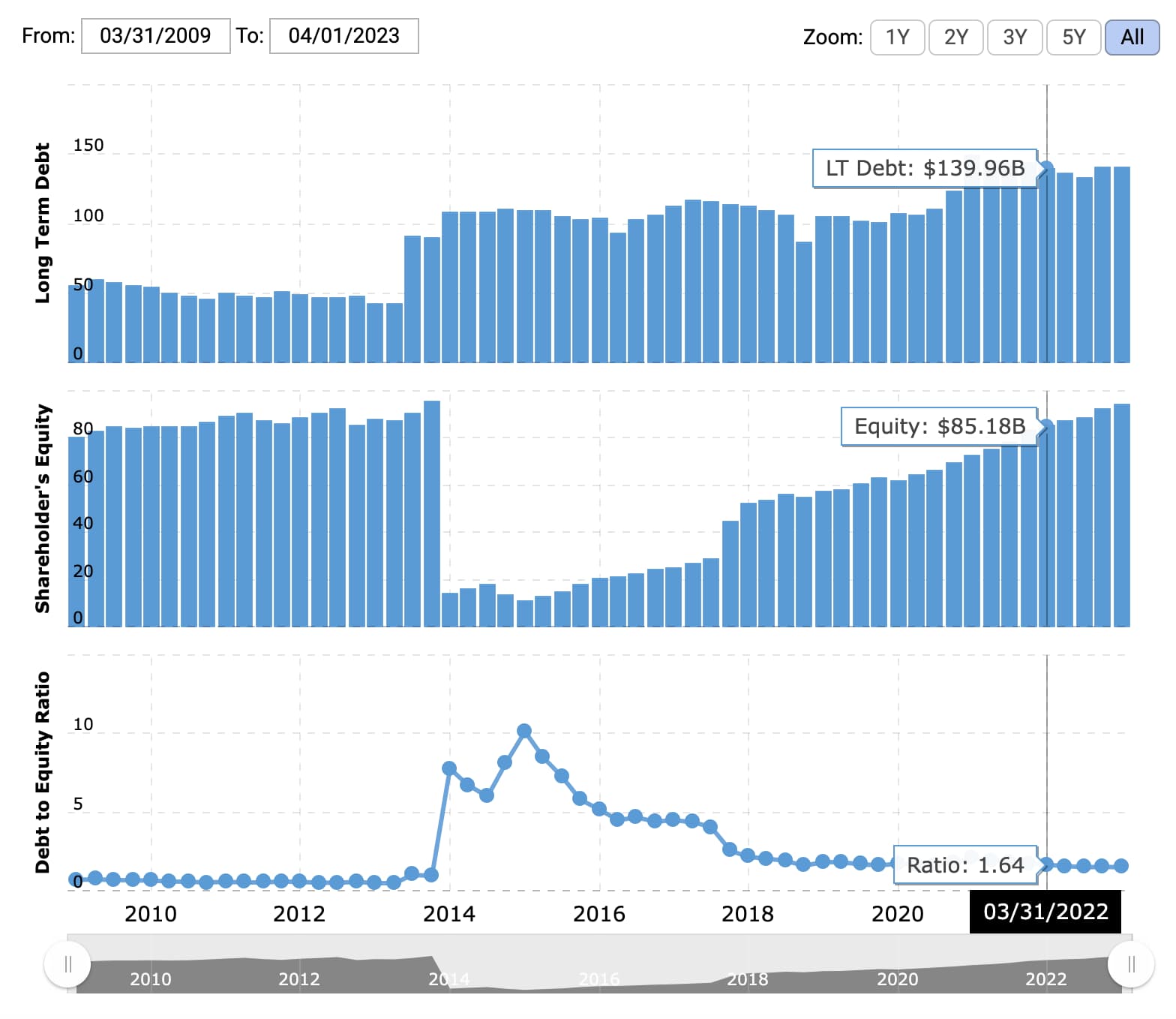
In 2015, Verizon made some sizable investments — together with allocating $28 billion for spectrum licenses and capital for future community capability — that took a big preliminary toll on stockholders’ fairness whereas including to its debt, resulting in an inflated debt-to-equity ratio. Nevertheless, as soon as these investments began paying off, Verizon’s monetary leverage ratio leveled out and returned to a decrease, extra reassuring determine in 2022.
Leverage Ratios Diagnos Enterprise Well being
If you happen to’re seeking to safe funding or simply need a greater understanding of how your online business would possibly fare going ahead, it is essential you’ve gotten a grasp in your leverage ratios. These figures could be very telling into your organization’s well being, potential, and skill to ship on its monetary obligations.
Editor’s notice: This put up was initially revealed in November, 2018 and has been up to date for comprehensiveness.